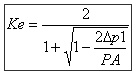| Air, Gas, Vapor, etc: Volume, density, viscosity, expansion. Correction of expansion, flow of correction according to the pressure and the temperature. |

| _You are in the heading |
|
|
For the compressible fluids (air, gas, steam, etc), the parameters "volume, density, viscosity", vary in a very significant way according to the pressure and of the temperature of use.
The density of a gas, which follows the Mariotte's Law, is given by the following formula:
For standard gases located at 0°C and 101325 Pa.
Density This density W is expressed in kg/m3 and has as an expression:
By stating a unit of flow such as normal m3 of a gas fluid, there
are two parameters which are critical for the definition of the
unit flow. They are the pressure and the temperature. All in all, the pressure is always 1013.25 mbar (KPa), 760 mm hectograms (hg) or 14.7 psia, which all are equivalent. However, the standard temperature changes from one country to another modifying to a significant degree the real flow. In Europe This indication means that the cubic meter is given under the conditions of temperature to 0°C, under an absolute pressure of 101300 Pascals, i.e. under the normal atmospheric pressure on the sea level. In USA This is even more confused in the manufacturers of the equipment
by using various names for the same unit or the same name for the
various units. Under the conditions of temperature and pressure of use, the correction of volume-flow compared to the flow of reference is carried out by the following formula:
V1 = (V2 x T1) / T2 With:
Contrary to calculations of the pressure losses for the liquid fluids (regarded practically as incompressible) the pressure loss due to the flow of a gas fluid (air, gas, steam, etc.) be accompanied by an expansion which results in an increase in the flow (i.e. speed), a reduction in the density and an increase in dynamic viscosity:
With in this expression:
The atmospheric pressure known as "normal", i.e. on the
sea level is 101 325 Pa The more we go up in altitude and the more the atmospheric pressure decreases. This pressure according to altitude has as a value:
The gain (or this loss) of relative pressure will be taken into account for the evaluation of the pressure losses on the open circuits, such as for example a gas feeding. With:
Last
update:
|
Copyright © 2003-2014 - ThermExcel - All Rights Reserved