| Functions of calculation written in VBA for the calculation of the properties of water and the steam. Function of calculation of pressure loss on the steam pipes. |
| _You are in the heading : |
|
|
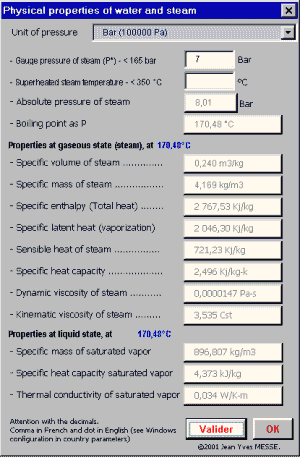
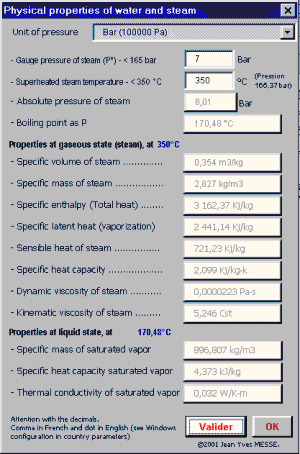
The module of integrated calculation makes it possible to establish all the physical characteristics of water, of vapor and of the vapor overheated
The calculation of the physical characteristics of the saturated
steam (1) can be done from the relative pressure or conversely according
to the temperature of the steam or the two parameters in the case
of use of the overheated steam (2) Functions of calculation written in VBA There is a great number of functions integrated available immediately in Excel. The personalized functions written in VBA for the ThermoVapeur program can be used like the functions integrated of Excel with the proviso that of installed the ThermoVapor program in Excel. The functions below are used in the sorter and can be re-used on
other worksheets. The functions below are used in the working file and can be re-used
on other worksheets. Formulas of computation of pressure
loss on the piping. Functions of calculation for the ThermoVapor program Calculation
of flow of water Calculation
of the Reynolds number according to the dynamic viscosity of the
fluid Calculation
of the Reynolds number according to cinematic viscosity Calculation
of the factor of friction according to the equation of Colebrook
(iterative Method) Speed of
water in m/s Calculation
of the dynamic Pressure Linear pressure
loss Correction
of expansion Calculation
of the module of pressure loss ( Coefficients K depend on the diameter
used) Functions for calculations of the properties of water and the steam See thematic: Vapor tables Kinematic viscosity
Dynamic viscosity
of water, value E-6. kg/(m S) Density of
the saturated steam in kg/m3 Density of
the overheated steam in kg/m3 Latent heat
of the saturated steam in kJ / kg K Latent heat
of the overheated steam in kJ / kg K Specific enthalpy
of the saturated steam (total heat) in kJ / kg K Specific enthalpy
of the overheated steam (total heat) in kJ / kg K Enthalpy of
ebullient water in kJ / kg K Enthalpy of
the water overheated in kJ / kg K Specific heat
of the steam in kJ / kg K Pressure of
vaporization in absolute bar Temperature
of vaporization Various functions Calculation
of the diaphragm (in mm) according to Standard NFX 10-101 Calculation
flow of vapor according the Kv Calculation
Kv-value of the valve for the vapor Conversion
pdc into modules Last
update:
|
Copyright © 2003-2014 - ThermExcel - All Rights Reserved